Rococo architecture is a mesmerizing expression of art that emerged from the heart of France in the 18th century. It represents an era of opulence, creativity, and complexity, echoing the aesthetic values of the nobility during its time. With its intricate designs, delicate ornamentation, and lively spirit, Rococo architecture stands out as a testament to the artistic evolution following the Baroque period, embracing a softer and more whimsical approach. This article will explore the various dimensions of Rococo architecture, its historical context, and its enduring influence on art and culture.
The Historical Context of Rococo Architecture

To truly appreciate Rococo architecture, one must delve into the historical backdrop against which it flourished. The roots of this style can be traced back to the early 18th century in France, where a shift in social dynamics and cultural trends gave rise to new artistic expressions.
The Transition from Baroque to Rococo
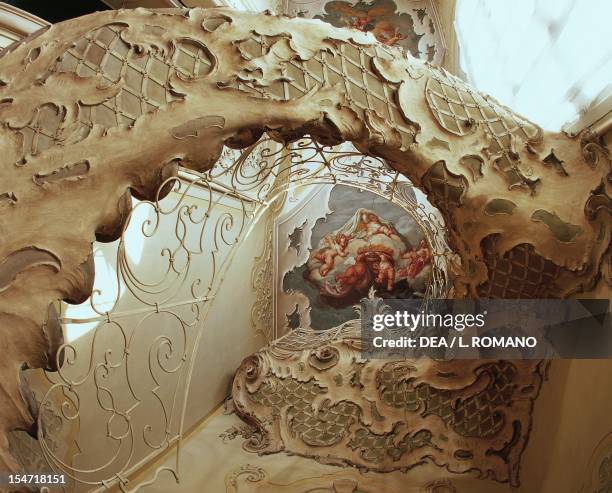
The transition from the grandiosity of the Baroque style to the more playful and ornate Rococo was a reflection of changing societal values.
The Baroque era was characterized by its dramatic use of light, bold colors, and imposing structures. It often embodied the power and authority of the church and monarchy. In contrast, Rococo emerged as a counterbalance to this heaviness, focusing on lightness, intimacy, and the celebration of everyday life.
This shift signified not only a change in architectural aesthetics but also a transformation in the way people engaged with their environments. Rococo architecture invited individuals into spaces designed for personal enjoyment and social interaction, reflecting the growing emphasis on leisure and pleasure among the upper classes.
The Influence of French Aristocracy
During the 18th century, the French aristocracy played a pivotal role in shaping Rococo architecture. The affluent elite sought to create lavish residences that showcased their wealth and sophisticated tastes.
Châteaux adorned with elaborate decorations, sumptuous gardens, and intimate salons became symbols of status. The influence of figures such as Madame de Pompadour, who appreciated the arts, fueled the Rococo movement, leading to the commissioning of exquisite palaces and interiors.
These extravagant settings were not only for show; they served as venues for social gatherings, balls, and other forms of entertainment, further embedding the essence of Rococo within the fabric of French high society.
Rococo’s Global Reach
While Rococo originated in France, its allure transcended borders, spreading across Europe and influencing various regions.
Countries like Germany, Austria, and Italy embraced the Rococo style, adapting it to their own cultural contexts. In Germany, for example, splendid churches and palaces reflected the Rococo ethos, emphasizing elegance and detail. Similarly, in Austria, notable architects like Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach contributed to the spread of this enchanting style through their innovative designs.
As Rococo architecture permeated different cultures, it took on unique characteristics, showcasing the adaptability of artistic movements in response to local traditions and preferences.
Characteristics of Rococo Architecture

Rococo architecture is distinguished by its exuberance, intricacy, and emotional appeal. Understanding the key features of this style allows us to recognize its significance and lasting impact on the world of design.
Ornate Decorations
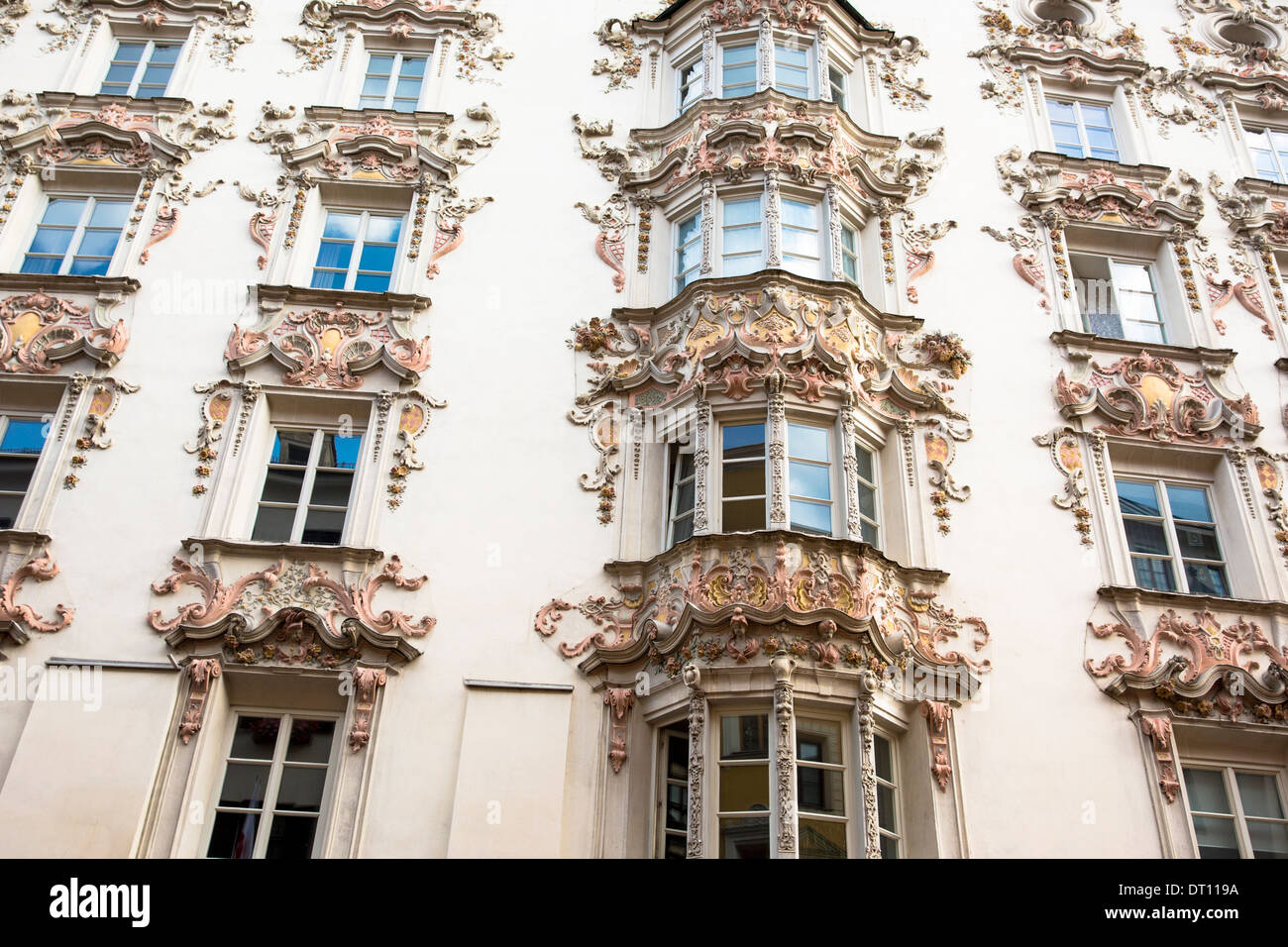

One of the most striking aspects of Rococo architecture is its emphasis on ornate decorations.
Architects and artisans of the Rococo period unleashed their creativity, crafting elaborate motifs, gilded moldings, and intricate stuccos. These embellishments appeared not only on facades but also within interiors, making every corner a visual delight.
The free-flowing lines and asymmetrical designs in Rococo ornamentation created a sense of movement, mimicking the natural forms found in nature. For instance, floral patterns, shells, and scrolls frequently adorned walls and ceilings, inviting viewers to engage with the space on a sensory level.
This decorative brilliance led to a harmonious relationship between art and daily life, ensuring that even mundane moments were infused with beauty.
Intimate Spaces

Unlike the grand and imposing structures of the Baroque era, Rococo architecture prioritized intimacy and comfort.
The layout of Rococo interiors often featured smaller rooms designed for personal interaction and relaxation. These spaces fostered social connections, encouraging gatherings among friends and family in warmly decorated salons or cozy dining areas.
The incorporation of soft furnishings, pastel color palettes, and carefully curated lighting further enhanced the inviting atmosphere. Rococo spaces exuded a sense of warmth and familiarity, contrasting sharply with the cold grandeur of earlier architectural styles.
Playful Light and Color
Color plays a crucial role in defining Rococo architecture.
Pastel shades—such as pale pinks, soft blues, and muted greens—permeate the palaces and salons of this style, creating an ethereal quality. These light hues evoke feelings of calmness and joy, resonating with the overall spirit of Rococo.
Moreover, the clever use of natural light is integral to Rococo design. Large windows and mirrors were strategically placed to maximize sunlight, illuminating the intricate details of the decor. This interplay between light and shadow added depth to spaces, enhancing the enchanting experience for occupants and visitors alike.
Integration of Art and Function

A hallmark of Rococo architecture is the seamless integration of art and function.
Every element within a Rococo building serves a purpose while simultaneously contributing to the overarching aesthetic narrative. From intricately designed furniture to hand-painted murals adorning walls, every detail is meticulously curated to create a cohesive environment.
This philosophy reflects a profound understanding of the relationship between art and life. Rococo architects aimed to elevate everyday experiences, transforming functional spaces into captivating realms filled with beauty and artistry.
The Cultural Significance of Rococo Architecture
The impact of Rococo architecture extends beyond its visual appeal; it played a significant role in shaping cultural practices and societal norms during its time.
A Reflection of Social Dynamics

Rococo architecture mirrored the shifting dynamics of society in the 18th century.
As France transitioned from feudalism to a more modern society, the architecture of the era began to reflect the aspirations and values of the burgeoning bourgeoisie. Wealthy merchants and newly affluent classes sought to emulate the lifestyles of the nobility, commissioning Rococo-inspired homes that emphasized comfort, elegance, and artistic flair.
This democratization of style signaled a departure from rigid class distinctions, allowing a broader segment of society to engage with and appreciate the arts. The availability of Rococo-inspired furniture and decorative items further bridged the gap between aristocracy and common citizens, fostering a shared appreciation for beauty.
The Role of Rococo in Arts and Entertainment

Beyond architecture, Rococo significantly influenced other forms of artistic expression, including painting, music, and theater.
The playful and ornate qualities of Rococo found resonance in the works of painters like Antoine Watteau, whose lively scenes captured the spirit of leisure and romance. In music, composers like François Couperin and Jean-Philippe Rameau embraced the Rococo ethos, creating compositions that mirrored the lightheartedness and charm of the architectural style.
Public spaces adorned in Rococo fashion—such as gardens, squares, and theaters—became vibrant hubs of cultural activities. People gathered to enjoy performances, socialize, and partake in leisurely pursuits, fostering a flourishing artistic community.
Critiques and Evolution of Rococo
Despite its popularity, Rococo architecture faced criticism from various quarters.
Some detractors viewed the style as excessive and frivolous, arguing that it represented a superficiality among the upper classes. This critique gained traction as societal changes set the stage for the emergence of Neoclassicism, which sought to return to the principles of ancient art and architecture.
However, rather than erasing Rococo from memory, this tension catalyzed an evolution of artistic expression. Elements of Rococo persisted within Neoclassical designs, blending the two approaches into a distinctive language that continued to resonate in subsequent periods.
The Enduring Legacy of Rococo Architecture
The legacy of Rococo architecture endures today, illustrating how artistic movements can transcend their original context and continue to inspire generations.
Rococo Revival Movements
Throughout history, there have been several revival movements that celebrated the essence of Rococo.
In the 19th century, the Rococo Revival—the trend of incorporating Rococo elements into contemporary designs—gained momentum. Architects and designers drew inspiration from the playful curves, ornamental details, and vibrant colors of Rococo, infusing these characteristics into new buildings and interiors.
This resurgence underscored the timeless appeal of Rococo, proving that its charm could adapt to modern sensibilities while maintaining the spirit of creativity and enjoyment.
Influences on Contemporary Design

Today, elements of Rococo architecture can be found in various aspects of contemporary design.
The emphasis on ornate details, curvilinear forms, and rich textures continues to inspire designers across multiple disciplines. Whether in luxury hotels, upscale restaurants, or residential interiors, the spirit of Rococo manifests itself in modern interpretations, showcasing a blend of nostalgia and innovation.
Furthermore, the emphasis on creating intimate and inviting spaces resonates with current trends in interior design, where comfort and aesthetics are paramount. As we navigate an increasingly fast-paced world, Rococo serves as a reminder of the importance of beauty, creativity, and connection in our living environments.
Cultural Reflections in Modern Society
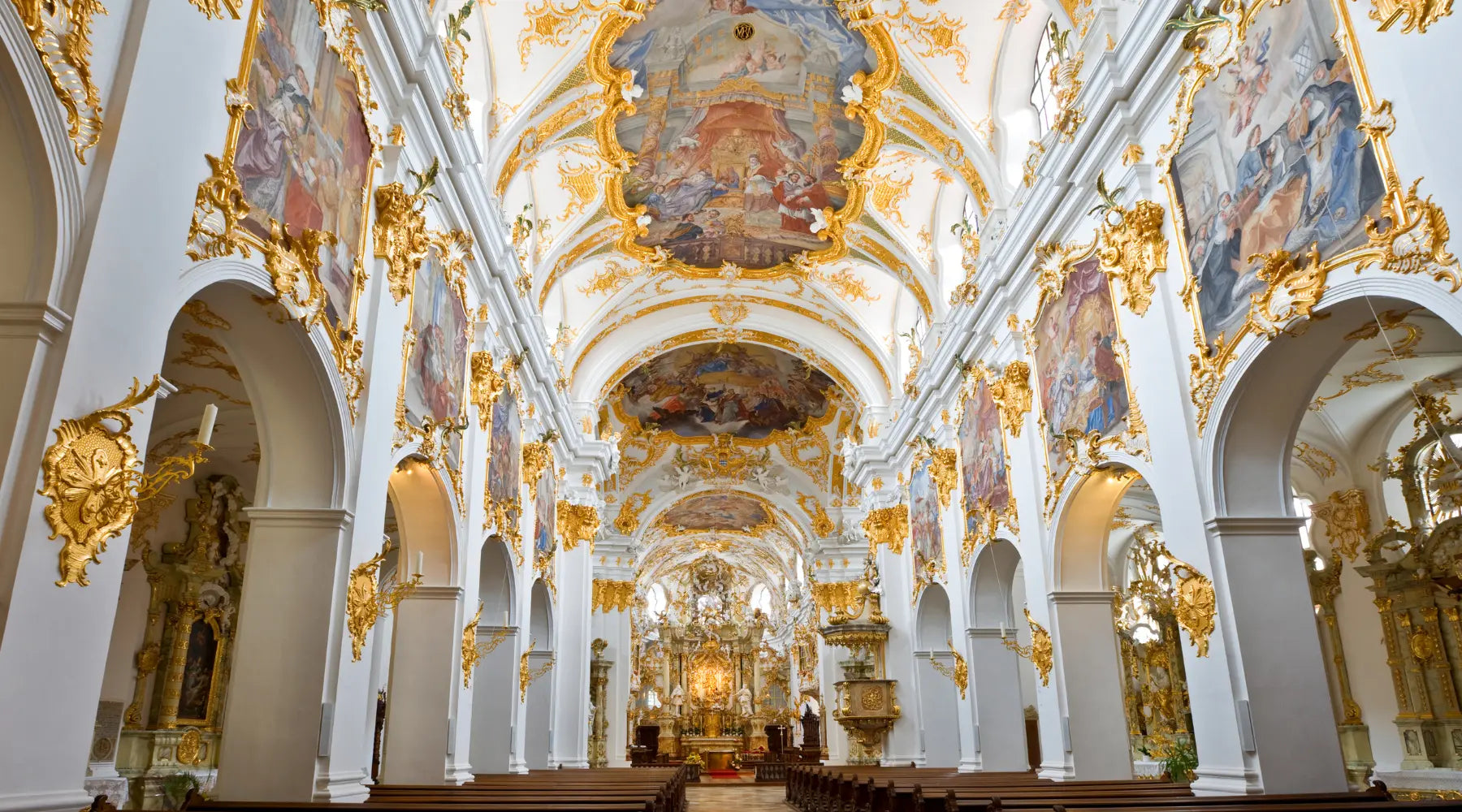

In a world grappling with rapid change, Rococo architecture offers valuable insights into the cultural significance of art and design.
By celebrating beauty and individuality, Rococo inspires modern creators to embrace their unique voices and challenge conventional norms. The spirit of experimentation and playfulness inherent in Rococo encourages artists, architects, and designers to push boundaries, fostering a culture of innovation and exploration.
In this sense, Rococo architecture acts as a bridge between past and present, inviting us to reflect on the relationship between art, society, and the human experience.
Conclusion
In summary, Rococo architecture is far more than a mere aesthetic; it represents a dynamic interplay between history, culture, and artistry. Through its intricate details, intimate spaces, and vibrant colors, Rococo invites us into a world where beauty reigns supreme and creativity knows no bounds. Its influence resonates across centuries, inspiring countless artists and architects to embrace the spirit of innovation and elegance.
As we admire the remnants of Rococo’s glory, let us celebrate its ability to elevate the ordinary, transform environments, and nurture connections among individuals. In doing so, we honor an artistic legacy that continues to enrich our lives today and reminds us of the profound impact of imagination on the human experience.
✉️ Stay Connected — Subscribe for Weekly Updates
Discover timeless stories, practical wisdom, and beautiful culture — delivered straight to your inbox.
*We only share valuable insights — no spam, ever.






